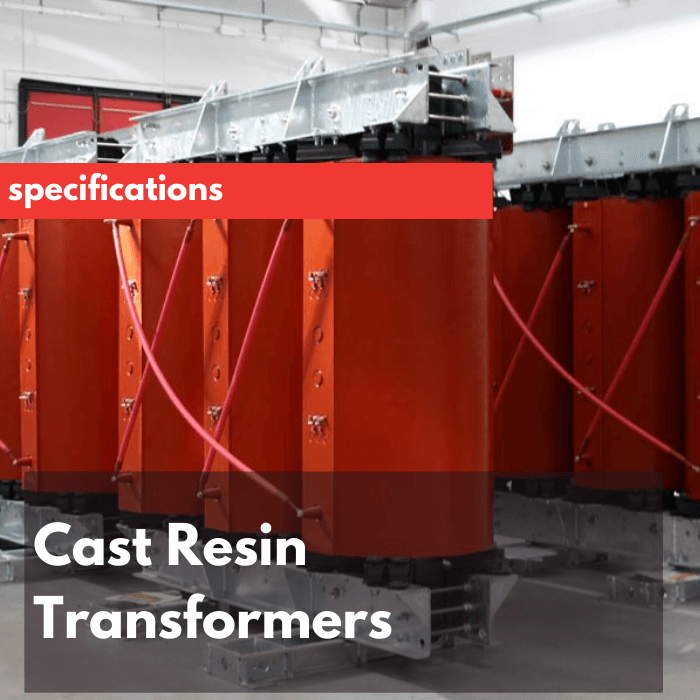
Cast Resin Transformer
Contact Us for quote
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
What is a Cast Resin Transformer?
A cast resin transformer is a static machine (without moving parts) designed to lower or raise voltage levels and galvanically separate those 2 voltage levels. Its windings are encapsulated in cast resin, and are cooled by natural air or forced ventilation, all safely without affecting the frequency, and require very little maintenance.
Cast resin transformers are usually installed in medium voltage, for all types of solutions: auxiliary services of electrical systems, substations, large factories or industrial plants, institution buildings, schools, shopping centers, residential energy supply and many other uses.
They are considered the most important electrical equipment in any electrical system, due to their function and cost, this is the reason why they must be protected to guarantee their operation and extend their life to máximum. We are experts manufacturing digital protection relays for cast resin transformers with hundreds of thousands of units distributed in a large number of countries, click on the following link to learn about our solution to protect cast resin transformers:
Cast Resin Dry Type Specification
A dry type transformer is a transformer that does not use liquid as insulation for its winding or core. Instead the windings and core are kept within a sealed cast epoxy resin.
Cast resin dry type transformers are used in high moisture areas. It is because its primary and secondary windings are encapsulated with epoxy resin (non hygroscopic). The encapsulation prevents moisture from penetrating the winding.
Available power 25 KVA to 12,500 KVA. with an insulation class of F (90oC Temp. Rise).
This type of transformer has some featured advantages. They are Better over load capacity.
Low partial discharge along with low loss. Hence efficiency is very good. As it is with non inflammable winding insulation, it offers zero risk to fire hazard. So it is suitable for indoor installation.
Can be fitted outdoor in IP 45 enclosure.
And off course non hygroscopic.
Vacuum Pressure Impregnated Transformer (VPI)
This type of transformer is made with minimum flammable material as insulation of windings. The windings of this transformer are made in foil or strip in a continuous layer. But for higher voltages, the winding is made of disks that are connected in series or parallel as per power rating with respect to voltage level.
The insulation of the winding is void free impregnation that is made with class H polyester resin. The primary and secondary winding with core are laced safely within a vacuum protective box. Moisture Ingress Protection is high and it never gets affected by moisture.
This type of transformer is available from 5KVA to 30MVA with insulation grade F(155oC) and H(180oC). It’s with Protection up to IP56.
This type of transformer has several advantages. They are-
High mechanical strength.
Void free insulation.
No temperature fluctuation.
Easy maintenance.
Less prone to fire hazard.
Cast Resin Transformer Maintenance Checklist
The following cheklist are essential for the maintenance of cast resin transformers:
- If the transformer has been stored for a long period, clean carefully LV and HV windings from dust, dirt and possible condensation.
- Clean the HV and LV windings from dust deposits, dirt and condensation. Use a vacuum cleaner to avoid dispersion of dirt and dust on the transformer.
- Make sure the room is dry, clean, with sufficient ventilation and without the risk of ingress of water.
- Check for temperature rise of coils on normal conditions.
Cast Resin Transformer vs Oil Transformer
Maintenance: Oil cooled transformers require more maintenance, and more often than dry-type. The oil needs to be sampled, but the dry type transformers do not contain oil.
Costs (Initial and Operating): Dry type has higher operating loss. Oil transformers have a better energy efficiency, and as a result longer lifespan.
Noise: Oil cooled transformers have a lower operating sound level.
Recyclability: Oil transformer has an easier core/coil reclamation.
Efficiency: Dry type transformers are larger, limited in voltage and size, making them overheat on overloads, higher electrical losses. Oil transformers are smaller and more efficient.
Voltage Capabilities: Dry transformers are designed for small to medium power applications (lower voltages than oil types). Oil transformers handle heavier loads, with higher voltages.
Location: Dry type is used in buildings, because they are environmentally safer, and are less flammable, ideal for shopping malls, hospitals, residential complexes. Oil transformers are used in outdoor installations due to the possibility of oil leakage with a higher fire risk, but these units are more environmentally friendly.
Oil units appear to be the better option overall with higher energy efficiency, recyclability, low noise pollution, lower operational costs and a small environmental foot print, but dry type is the best and many times required option for commercial and indoor operations, because they are safer units to operate around people.
Cast Resin Transformer Tap Changer
A tap changer is a busbar arrangement to change the output voltage of a transformer. By altering the number of turns in transformer winding there will be a change to the turns ratio of the transformer. Required in many applications where the medium voltage is not nominal.
Types: de-energized tap changer (DETC) and an on-load tap changer (LTC)
Cast Resin Transformer Dimensions and Weight
| Power KVA | Length mm | Width mm | Height mm | Total Weight kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 920 | 670 | 1050 | 550 |
| 400 | 1300 | 820 | 1400 | 1200 |
| 800 | 1600 | 820 | 1450 | 1900 |
| 1000 | 1600 | 980 | 1600 | 2150 |
Cast Resin MV LV Transformer
Cast resin transformers have the HV winding embedded in a cast resin body using vacuum-encapsulated moulds. Mainly used as auxiliary Transformer in substations for transport, industry and commercial applications. Highly reliable and safe to use indoors.
3 Phase Cast Resin Transformer
These transformers are made with a magnetic core from laminated grain-oriented silicon steel. Additionally, HV winding can also be wound from insulated by an inter-layer film, pre-impregnated with heat-activated epoxy resin. The ends of the windings are protected and insulated using Class F materials. With outstanding resistance to harsh industrial atmospheres, excellent dielectric withstand and very good resistance to short-circuit conditions are ideal for industrial and commercial use.
Temperature Rise for Cast Resin Transformer
The IEC standard specifies that a transformer with insulation class F must withstand a short- time temperature of 180°C without suffering immediately damage. Nominal operating temperature is based on the LV winding (120°C - 150°C), depending on the winding temperature rise, referred to the maximum ambient temperature of 40°C specified according to VDE 0532, part 6.